Indoor air pollution is a critical health issue, often more severe than its outdoor counterpart, and adversely affects millions of people worldwide. While we often associate air pollution with external sources, the air inside our homes and offices can be even more polluted due to the concentration of toxins. Understanding and mitigating the most common indoor air pollutants is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment. Here you will find a detailed overview of five common sources of indoor air pollutants and effective strategies to combat them.
1. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
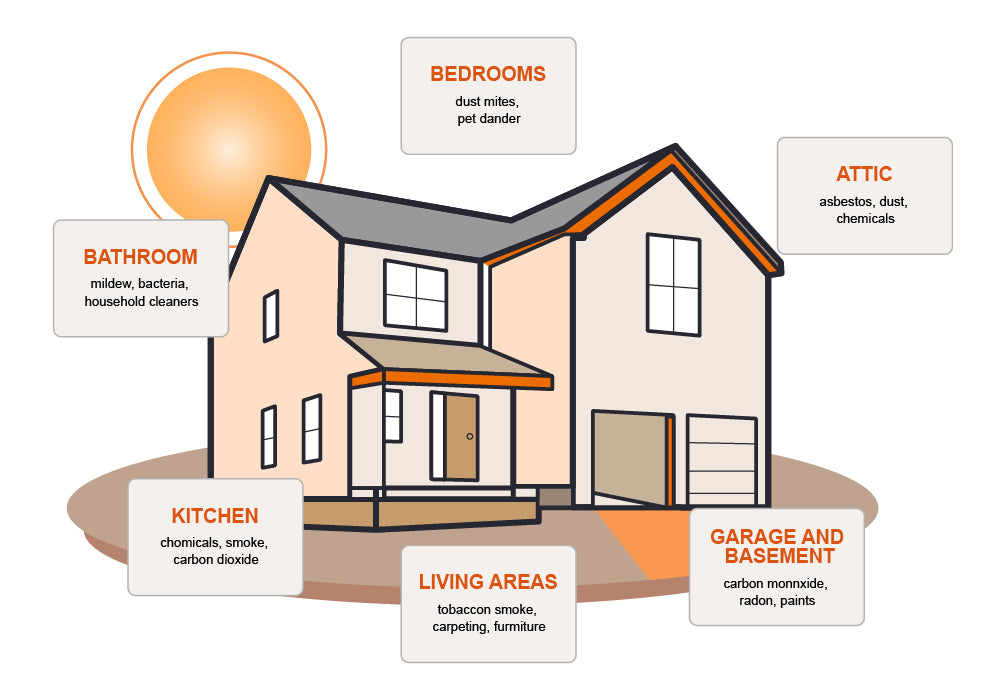
Sources and Risks: Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fossil fuels such as gas, oil, wood, and coal. Common household sources include heating systems, stoves, and vehicles running in attached garages. CO impedes the blood's ability to carry oxygen and can cause severe health effects such as headaches, dizziness, confusion, and even death at high levels.
Mitigation Strategies:
Ensure proper installation and maintenance of all fuel-burning appliances.
Use CO detectors near sleeping areas and check them regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Improve ventilation in areas where combustion occurs to prevent CO buildup.
2. Tobacco Smoke
Sources and Risks: Tobacco smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are toxic and carcinogenic. Smoking indoors significantly increases the risk of respiratory infections, lung cancer, and heart disease among smokers and non-smokers alike.
Mitigation Strategies:
Enforce a strict no-smoking policy inside the home.
Maintain clean air filters and use air purifiers with activated carbon filters to remove harmful gases from the indoor air.
3. Pet Dander
Sources and Risks: Pet dander is tiny, microscopic flakes of skin shed by cats, dogs, and other furry or feathered pets. It is a common allergen that can cause allergic reactions and exacerbate asthma symptoms.
Mitigation Strategies:
Regularly bathe and groom pets to minimize the release of dander.
Vacuum frequently uses a vacuum cleaner equipped with a HEPA filter.
Keep pets out of bedrooms and other areas where you spend a lot of time to limit exposure.
4. Mold and Mildew
Sources and Risks: Mold and mildew thrive in damp and humid environments and can cause a variety of health problems, including allergies, asthma, and other respiratory issues. Common places for mold growth include bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
Mitigation Strategies:
Control humidity levels in your home, ideally between 30-50%, using dehumidifiers and air conditioners.
Fix leaks and improve drainage around the house to prevent water accumulation. Clean and dry any wet areas within 24-48 hours to prevent mold growth.
5. Radon
Sources and Risks: Radon is a radioactive gas that naturally emanates from the earth and can accumulate in homes, especially in basements and ground floors. It is the second leading cause of lung cancer, making it a silent but deadly pollutant.
Mitigation Strategies:
Test your home for radon using a radon test kit available at hardware stores or online.
Seal cracks and openings in your home’s foundation and floors to reduce radon infiltration.
Consider a radon mitigation system if your radon levels are high, which can include sub-slab depressurization or increased ventilation.
6. Lead Particles
Sources and Risks: Older homes built before the ban on lead-based paints in 1978 are particularly at risk of indoor lead pollution. Lead dust can be released from deteriorating paint or during renovations, posing serious health risks, particularly to children, including brain damage and developmental delays.
Mitigation Strategies:
Test your home for lead if it was built before 1978.
Use wet cleaning approaches to remove lead particles from surfaces.
Hire certified professionals to remove lead-based paint or contain it with special sealants safely.
General Tips to Improve Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment, especially since most people spend a significant amount of time indoors. Here are some general tips that can help you enhance the air quality in your home:
1. Ventilation
Increase Air Flow: Regularly open windows and doors to allow fresh air to circulate and dilute indoor pollutants, unless outdoor air quality is poor.
Use Exhaust Fans: Install and use exhaust fans in the kitchen and bathrooms to remove pollutants directly from these areas and prevent their spread to other parts of the home.
2. Keep It Clean
Regular Cleaning: Dust and vacuum your home frequently using a vacuum cleaner equipped with a HEPA filter to trap dust particles, pet dander, and other allergens.
Declutter: Reduce clutter to minimize dust and make cleaning easier. Clutter can trap and hold dust that can trigger allergies and respiratory problems.
3. Air Purification

Air Purifiers: Invest in a whole house air purifier to remove particulate matter and other pollutants from the air.
No Smoking: Enforce a strict no-smoking policy inside the home to prevent tobacco smoke, a major indoor pollutant, from affecting poor indoor air quality.
4. Reduce Chemical Pollutants
Avoid Synthetic Fragrances: Use natural products whenever possible, as many air fresheners and scented candles release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other chemicals into the air.
Safe Cleaning Products: To reduce exposure to harsh chemicals, choose cleaning products that are labeled "low VOC" and are environmentally friendly.
5. Green Your Space
Indoor Plants: Some plants are known to purify the air naturally. Plants like spider plants, peace lilies, and snake plants absorb carbon dioxide and remove toxins such as benzene, formaldehyde, and trichloroethylene.
Sustainable Materials: When renovating or decorating, choose materials that emit fewer chemical pollutants, such as low-VOC paints, and sustainable flooring options like bamboo or cork.
6. Regular Maintenance of HVAC System
Change Filters Regularly: To maintain airflow and pollutant removal efficiency, ensure that you replace HVAC filters at recommended intervals or more frequently if necessary.
Annual Inspections: Have your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system inspected and serviced by a professional at least once a year to ensure it is functioning properly and not contributing to indoor air pollution.
Conclusion
By understanding these common indoor air pollutants and implementing effective strategies to combat them, you can improve the air quality in your home, ensuring a healthier environment for you and your family.
Also, it is worth noting that improving air quality in your home isn't enough to ensure you or your family are healthy, especially after experiencing bad air quality. Visit the hospital to let a doctor check your health status.

